Sex-linked disorders - Higher
All genetic conditions are called disorders and those that inherit them are called sufferers. Most genetic disorders, like cystic fibrosis, require two recessiveDescribes the variant of a gene for a particular characteristic which is masked or suppressed in the presence of the dominant variant. A recessive gene will remain dormant unless it is paired with another recessive gene. alleles to be inherited (one from the mother and one from the father). So if a person inherited both recessive alleles they would be a sufferer. If a person receives only one recessive allele, their one dominantAn allele that always expresses itself whether it is partnered by a recessive allele or by another like itself. allele means they do not have symptoms of the disorder. However, they are able to pass it to their children. They are called a carrier.
If alleles for a disorder appear on the sex chromosomes they are called sex-linked. Men have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. The Y chromosome is smaller than the X chromosome and does not possess as many genes. If a gene is contained on the part of the X chromosome that is missing from the Y chromosome, men only have one allele for that gene, rather than the usual two. If the allele on the X chromosome codes for a disorder, the man will always have the disorder because there isn't another allele on the Y chromosome to mask the effect of the allele. This means that even conditions caused by a recessive allele will be inherited by the man because there cannot possibly be a dominant allele on the X chromosome to mask the effect of that recessive allele.
Red-green colour blindness
This disorder affects about 8% of men and about 1% of women. Sufferers are unable to tell the difference between red and green. Tests like the image below are used to test for this disorder.
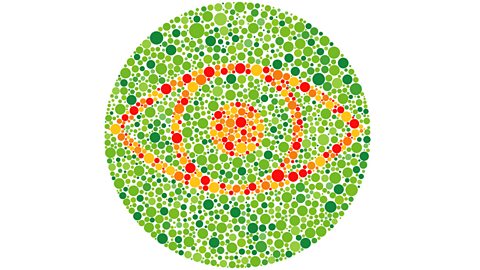
The female alleles are shown in the top row and the male alleles are shown in the left-hand column
| Xb | XB | |
| XB | XBXb | XBXB |
| Y | YXb | YXB |
| XB | |
|---|---|
| Xb | XBXb |
| XB | XBXB |
| Y | |
|---|---|
| Xb | YXb |
| XB | YXB |
B represents the dominant allele for unaffected.
b represents the recessive allele for red-green colour blindness.
These alleles are found on the X chromosome. The smaller Y chromosome does not carry an allele for the colour blindness gene.
The male genotype is XBY which means he does not have the disorder. The female genotype is XbXB which means she is a carrier for the disorder.
Of the possible offspring:
- 25% are XBXb which are female carriers without colour blindness
- 25% are XBXB which are females with colour blindness
- 25% are YXb which are males without colour blindness
- 25% are YXB which are males with colour blindness
Note that the Y chromosome does not have the superscript letter B or b because it does not possess the allele for colour blindness.
Question 1
Question
Draw a Punnet square to show the outcome between a cross of a male sufferer of colour blindness and a female carrier. Give your results as percentages and explain what the genotype means for each different example.
In this diagram the female alleles are shown in the top row and the male alleles are shown in the left-hand column
| Xb | XB | |
| XB | XBXb | XBXB |
| Y | YXb | YXB |
| XB | |
|---|---|
| Xb | XBXb |
| XB | XBXB |
| Y | |
|---|---|
| Xb | YXb |
| XB | YXB |
Of the possible offspring:
- 25% are XBXb which are female carriers without colour blindness
- 25% are XbXb which are females without colour blindness
- 25% are YXb which are males with colour blindness
- 25% are YXB which are males without colour blindness.