Exam practice
GCSE Biology: exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Biology past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.

GCSE Biology: exam-style questions
Edexcel GCSE foundation and higher triple science exam practice with Bitesize interactive quizzes covering feedback and common errors in cells, organisation and more.

GCSE Biology: quick-fire questions
Foundation and higher exam quiz based on Edexcel GCSE biology past papers to boost your revision in photosynthesis, respiration, plant disease and more.

Quizzes
QUIZ: Cell structure
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology students studying cells and their structures.
QUIZ: Types of cell
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying cells and the different cell types.
QUIZ: Cell division
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology students studying cell division and the process of mitosis.
QUIZ: Transport in cells
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying transport in and out of cells.
QUIZ: The nervous system
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying the nervous system and how it enables humans to coordinate movement.

QUIZ: The human endocrine system
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying the human endocrine system and the role hormones play.
QUIZ: Hormones in human reproduction
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying the role hormones play in human reproduction.

QUIZ: Homeostasis in humans
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying homeostasis and how important it is to regulation of the body.

QUIZ: Plant hormones
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying hormones and how they promote growth in plants.
QUIZ: Communicable diseases activity 1
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying communicable diseases, including the viruses, bacteria and protists that can cause them.

QUIZ: Communicable diseases: prevention
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying communicable diseases and how the body and medicine work to prevent them.

QUIZ: Vaccinations and antibiotics
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying treating and preventing diseases - through the provision of vaccinations and antibiotics.

QUIZ: Bacterial growth and drug discovery
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying bacterial growth and how medicines have been developed to fight illness.
QUIZ: Plant organisation activity 1
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying plant structures, their functions and how substances are transported in and out of a plant.
QUIZ: Plant organisation activity 2
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying plant organisation, exploring processes such as transpiration and osmosis.

QUIZ: Non-communicable diseases activity 1
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying non-communicable diseases such as Type 2 diabetes and tumours.

QUIZ: Non-communicable diseases: data analysis
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying non-communicable diseases and the role data analysis plays in reporting statistics.

QUIZ: Decomposition
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying decomposition and the rate of decay under various circumstances.
QUIZ: Biodiversity and the effect of human interaction on ecosystems
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying biodiversity and the impact human activity has on it.

QUIZ: Food production
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying food production and how various factors affect productivity.
Podcasts
The Cell
All living things are made of cells, which is why they’re called the building blocks of life.

The organisation of plants and animals
Learn all about plant and animal organisation with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Infection and response
Learn all about infection and response for your GCSE biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Homeostasis
Learn all about homeostasis for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Inheritance, variation and evolution
Learn all about inheritance, variation and evolution for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Ecology
Learn all about ecology for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Science exam techniques
Learn all about science exam techniques for your GCSE science exams with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Key concepts in biology
Cell structure - Edexcel
Light and electron microscopes allow us to see inside cells. Plant, animal and bacterial cells have smaller components each with a specific function.
Enzymes - Edexcel
Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up reactions. They are specific for their substrate. The lock and key hypothesis models this. Enzymes are denatured at extremes of temperature and pH.

Transport in cells - Edexcel
Diffusion is the movement of particles from a high to lower concentration. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane. Active transport moves particles from low to higher concentration.
Sample exam questions - key concepts in biology - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Cells and control
Cell division - Edexcel
Mitosis is a type of cell division which produces two identical diploid daughter cells. Cancerous tumours are either malignant or benign. Specialised cells are formed when stem cells differentiate.
Coordination and control - The nervous system - Edexcel
The nervous system enables humans to react to their surroundings and to coordinate their behaviour. It comprises billions of neurones, and it uses electrical impulses to communicate very quickly.
Sample exam questions - cells and control - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Genetics
Reproduction, the genome and gene expression - Edexcel
The differences between sexual and asexual reproduction, the structure of DNA and its role in making proteins, mutations and their effects and how characteristics are inherited.

Genetic inheritance - part one - Edexcel
Mutations can cause a permanent change in the DNA of an organism. In the 19th century, Gregor Mendel determined rules to explain genetic inheritance using pea plants. Genetic crosses using Punnett squares show how likely offspring are to inherit characteristics from their parents.

Genetic inheritance - part two - Edexcel
We inherit our sex (male or female) and blood group from our parents. Genetic disorders can also be inherited. Selective breeding occurs when humans breed plants and animals for specific characteristics. Cloning (often in plants and not in humans) makes genetically identical copies of the one parent organism.

Sample exam questions - genetics - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Natural selection and genetic modification
Evolution - Edexcel
Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution by natural selection. All living species are classified using the system developed by Linnaeus.

Genetic modification - Edexcel
Genetic modification are techniques used to remove a gene or genes from one species and place into another. There are benefits and risks to this process.

Sample exam questions - natural selection - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Health, disease and the development of medicines
Communicable disease - Edexcel
Disease-causing viruses, bacteria, fungi or protists are called pathogens. Sterilising water, preparing food hygienically, washing, vaccination and barrier contraception can reduce the spread of pathogens.
Plant disease - Edexcel
Pathogens are disease-causing viruses, bacteria, fungi or protists. Some pathogens infect plants and others infect animals. Plants have physical and chemical defences against pathogens.

Treating, curing and preventing disease - Edexcel
The immune system defends humans from pathogens. Physical and chemical barriers prevent infection. White blood cells attack pathogens. Immunisations usually involve injecting inactive pathogens.

Making medicines - Edexcel
The development of drugs is a long, complicated and expensive process. Monoclonal antibodies are identical copies of an antibody. They are used in pregnancy tests and in cancer treatment.
Non-communicable diseases - Edexcel
Non-communicable diseases are not transferred between people, eg cancer, diabetes, genetic and neurological disorders and heart disease. Risk factors increase the chances of developing these diseases.
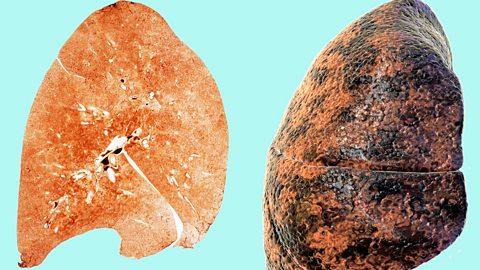
Sample exam questions - health, disease and medicine development
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Plant structures and their functions
Photosynthesis - Edexcel
Green plants and algae use light energy to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. Temperature, carbon dioxide concentration and light intensity can affect the rate of photosynthesis.

Plant organisation - Edexcel
Plant leaves are adapted for photosynthesis and gas exchange. Roots absorb water and mineral ions through root hair cells and are transported up the plant by the xylem.
Plant hormones - Edexcel
Hormones promote growth within plants. Plant hormones are unequally distributed throughout the stems and roots, which results in parts of the plant growing in a particular direction.

Sample exam questions - plant structures and their functions - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Animal coordination, control and homeostasis
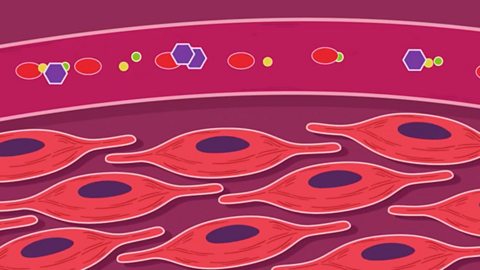
Coordination and control - The human endocrine system - Edexcel
The endocrine system secretes hormones into the bloodstream from glands throughout the body. Hormones travel in the blood stream to specific target organs, where they have an effect.
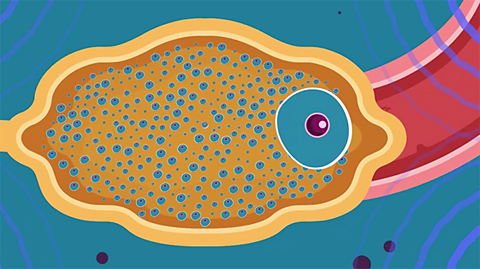
Hormones in human reproduction - Edexcel
Hormones regulate the menstrual cycle. This involves the monthly release of an egg from the ovary and the build-up and breakdown of the lining of the uterus.
Homeostasis in humans - Edexcel
Homeostasis is the regulation of internal conditions inside cells or organisms, to create the optimum conditions for cell function.

Sample exam questions - coordination, control & homeostasis - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Exchange and transport in animals
Gas exchange in animals - Edexcel
For an organism to function, substances must move into and out of cells. Three processes contribute to this movement – diffusion, osmosis and active transport.
Cellular respiration and transport - Edexcel
The circulatory system transports substances between the exchange surface and cells. It delivers oxygen and glucose to the tissues for respiration, which is the release of energy to cells.
Sample exam questions - exchange and transport in animals - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Ecosystems and material cycles
Adaptations, interdependence and competition - Edexcel
Organisms depend on each other for survival. This is called interdependence. Both living and non-living factors will affect the abundance and distribution of organisms in a habitat.

Organisation of an ecosystem - Edexcel
The feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem can be seen in food chains. Sampling allows us to measure the abundance and distribution of these species.

Biodiversity & the effect of human interaction on ecosystems - Edexcel
Biodiversity is a measure of how many different species live in an ecosystem. Human activities like changing land use, deforestation and peat bog destruction reduce this.
Biological factors affecting food security - Edexcel
Factors such as the increase in human population, new pests and pathogens and armed conflict, can result in food scarcity. Improved farming techniques and sustainable fisheries can help increase supply.

Natural cycles and decomposition - Edexcel
Materials such as carbon, nitrogen and water are recycled in the ecosystem. When organisms die, decomposition will recycle minerals and nutrients back to the environment.

Sample exam questions - ecosystems and material cycles - Edexcel
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Practical skills
Practical skills
Scientific investigations have several stages - planning, collecting data, analysing data and evaluation. It is important to understand how to carry out each stage of the investigation.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription