Exam practice
GCSE Biology: exam-style quiz by topic
Try this quiz based on GCSE Biology past papers. Choose the topic you would like to revise and answer the questions.

GCSE Biology: exam-style questions
OCR Gateway GCSE foundation and higher triple science exam practice with Bitesize interactive quizzes covering feedback and common errors in cells, organisation and more.

GCSE Biology: quick-fire questions
Foundation and higher exam quiz based on OCR Gateway GCSE biology past papers to boost your revision in photosynthesis, respiration, plant disease and more.

Quizzes
QUIZ: Cell structure
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology students studying cells and their structures.
QUIZ: Types of cell
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying cells and the different cell types.
QUIZ: Cell division
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology students studying cell division and the process of mitosis.
QUIZ: Transport in cells
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying transport in and out of cells.
QUIZ: The nervous system
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying the nervous system and how it enables humans to coordinate movement.

QUIZ: The human endocrine system
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying the human endocrine system and the role hormones play.
QUIZ: Plant hormones
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying hormones and how they promote growth in plants.
QUIZ: Communicable diseases activity 1
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying communicable diseases, including the viruses, bacteria and protists that can cause them.

QUIZ: Communicable diseases: prevention
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying communicable diseases and how the body and medicine work to prevent them.

QUIZ: Vaccinations and antibiotics
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying treating and preventing diseases - through the provision of vaccinations and antibiotics.

QUIZ: Bacterial growth and drug discovery
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying bacterial growth and how medicines have been developed to fight illness.
QUIZ: Plant disease
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying the physical and chemical defences plants have to combat diseases.
QUIZ: Plant organisation activity 1
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying plant structures, their functions and how substances are transported in and out of a plant.
QUIZ: Plant organisation activity 2
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying plant organisation, exploring processes such as transpiration and osmosis.

QUIZ: Non-communicable diseases activity 1
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying non-communicable diseases such as Type 2 diabetes and tumours.

QUIZ: Non-communicable diseases: data analysis
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying non-communicable diseases and the role data analysis plays in reporting statistics.

QUIZ: Genes and inheritance
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying genes and inheritance and how the latter controls the characteristics of living things.
QUIZ: Inherited disorders and genetic testing
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying inherited diseases and genetic testing.
QUIZ: Biodiversity and the effect of human interaction on ecosystems
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying biodiversity and the impact human activity has on it.

QUIZ: Food production
This interactive quiz is suitable for GCSE Biology (single science) students studying food production and how various factors affect productivity.
Podcasts
The Cell
All living things are made of cells, which is why they鈥檙e called the building blocks of life.

The organisation of plants and animals
Learn all about plant and animal organisation with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Infection and response
Learn all about infection and response for your GCSE biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Homeostasis
Learn all about homeostasis for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Inheritance, variation and evolution
Learn all about inheritance, variation and evolution for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Ecology
Learn all about ecology for your GCSE Biology exam with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Science exam techniques
Learn all about science exam techniques for your GCSE science exams with Dr Alex Lathbridge.

Cell level systems
Cell structures - OCR Gateway
Organisms are made of cells. Most organisms are multicellular and have cells that are specialised to do a particular job. Microscopes produce magnified images of cells so we can study them in detail.
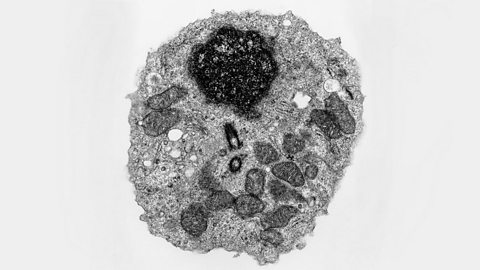
What happens in cells (and what do cells need)? - OCR Gateway
The genetic code of all life on Earth is made from DNA. Proteins like enzymes and hormones are made during protein synthesis. Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up chemical reactions.
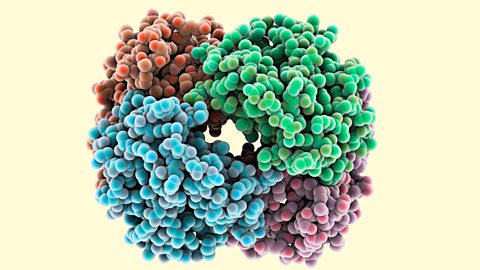
Respiration - OCR Gateway
Respiration releases energy from glucose in the form of ATP. This occurs in all living cells. Aerobic respiration (with oxygen) releases more energy than anaerobic respiration (without oxygen). In this study guide you will learn about aerobic and anaerobic respiration, the aerobic respiration word equation and metabolism in plants and animals.

Photosynthesis - OCR Gateway
Plants make food using photosynthesis. This food is important for the plants themselves and for organisms that feed on plants. Getting optimum rates of photosynthesis produces maximum plant yields.

Sample exam questions - cell level systems - OCR Gateway
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Scaling up
Supplying the cell - OCR Gateway
For an organism to function, substances must move into and out of cells. Three processes contribute to this movement - diffusion, osmosis and active transport.

Mitosis and cell specialisation - OCR Gateway
Mitosis is cell division which produces two identical diploid cells for growth and repair. Differentiation occurs when cells become specialised. Stem cells can develop into different cell types.
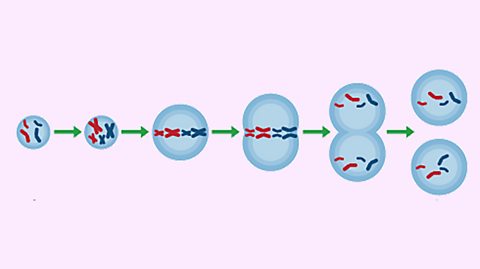
The challenges of size in animals - OCR Gateway
Larger animals have a lower surface area to volume ratio. This means they need transport systems like our circulatory system and exchange surfaces like our lungs or fish gills.
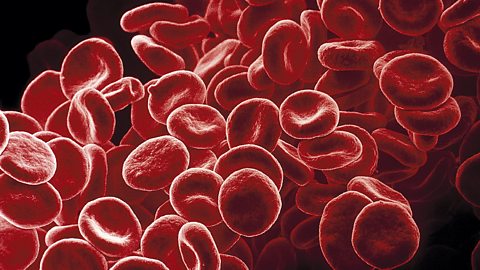
The challenges of size in plants - OCR Gateway
During transpiration plants move water from the roots to their leaves for photosynthesis in xylem vessels. Glucose made in photosynthesis is then moved to all cells in phloem vessels for respiration.

Sample exam questions - scaling up - OCR Gateway
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Organism level systems
Coordination and control - The nervous system - OCR Gateway
The nervous system allows us to react to our surroundings very quickly and to coordinate our behavior. It comprises millions of neurones and electrical impulses pass along them very quickly.
Coordination and control - The endocrine system - OCR Gateway
The endocrine system secretes hormones into the bloodstream from glands throughout the body. Hormones produce an effect on specific target organs in the body.

Plant hormones - OCR Gateway
Hormones control important processes like germination, flower opening, dropping leaves, phototropism and geotropism. We use plant hormones in weedkillers, and to make seedless fruit and root cuttings.

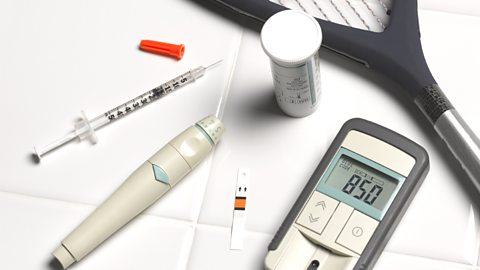
Maintaining internal environments - OCR Gateway
Homeostasis is the regulation of conditions in the body such as temperature, water content and carbon dioxide levels. Diabetes is a condition where the body cannot regulate its blood glucose levels.
Sample exam questions - organism level systems - OCR Gateway
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Community level systems
Material cycling in ecosystems - OCR Gateway
Materials on Earth cycle between living organisms and the environment. Microorganisms are vital for these cycles. They break down dead matter and release the materials back to the environment.

Organisation in ecosystems - OCR Gateway
Organisms interact with and rely on one another to survive. They also rely on a stable environment. Changes to organism numbers and the environment can determine whether an organism will live or die.

Sample exam questions - community level systems - OCR Gateway
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Genes, inheritance and selection
Inheritance - OCR Gateway
Our genes are inherited from our parents, and the different combinations of these genes make us unique. Genetic inheritance controls the characteristics of all living things.

Natural selection and evolution - OCR Gateway
Genetic variation, as well as changes in the environment, cause characteristics of organisms to change over time. This process of natural selection leads to the evolution of new species.

Sample exam questions - genes, inheritance and selection - OCR Gateway
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Global challenges
Field investigations - OCR Gateway
Ecologists study the distribution of living organisms in habitats to find out how healthy it is. They use many different sampling methods to provide quantitative data which is then analysed.

Monitoring and maintaining the environment - OCR Gateway
Biodiversity is a measure of how many different species live in an ecosystem. Human activities like changing land use, deforestation and peat bog destruction reduce this.

Feeding the human race - OCR Gateway
Factors such as the increase in population, new pathogens and overhunting can result in food scarcity. Improved farming techniques, sustainable fisheries and biotechnology can help increase supply.

Monitoring & maintaining health - Communicable diseases - OCR Gateway
Health is the state of physical and mental well-being. Factors can work together to both physical and mental health. A disease is a disorder that affects an organism鈥檚 body, organs, tissues or cells.
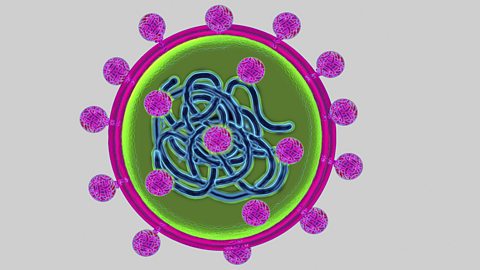
Treating, curing and preventing disease - OCR Gateway
Pathogens are everywhere. The body has evolved defences that act to prevent pathogens entering it. If a pathogen does enter the body then the immune system helps to fight it off.
Monoclonal antibodies - Higher - OCR Gateway
Monoclonal antibodies are identical copies of one type of antibody. They are incredibly useful in medicine for diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Plant disease - OCR Gateway
Pathogens are disease-causing viruses, bacteria, fungi or protists, which attack plants as well as animals. Plants have physical and chemical defences against pathogens.

Cancer and cardiovascular disease - Non-communicable - OCR Gateway
The chance of developing a non-communicable disease can be increased or decreased depending upon a person鈥檚 lifestyle or the genes they inherit. Two common types are cancer & cardiovascular disease.

Monitoring and maintaining health - Non-communicable - OCR Gateway
Scientists find links between diseases and their causes. The information is used to reduce the number of people with the disease by giving lifestyle advice or developing new ways to fight the disease.

Sample exam questions - global challenges - OCR Gateway
Understanding how to approach exam questions helps to boost exam performance. Question types will include multiple choice, structured, mathematical and practical questions.

Practical skills
Practical skills
Scientific investigations have several stages - planning, collecting data, analysing data and evaluation. It is important to understand how to carry out each stage of the investigation.

Links
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription
- External linkExternal link
- External linkExternal link
- SubscriptionSubscription